Identification of infectious agents in early marine Chinook and Coho salmon associated with cohort survival
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Methods overview
Juvenile salmon sampling
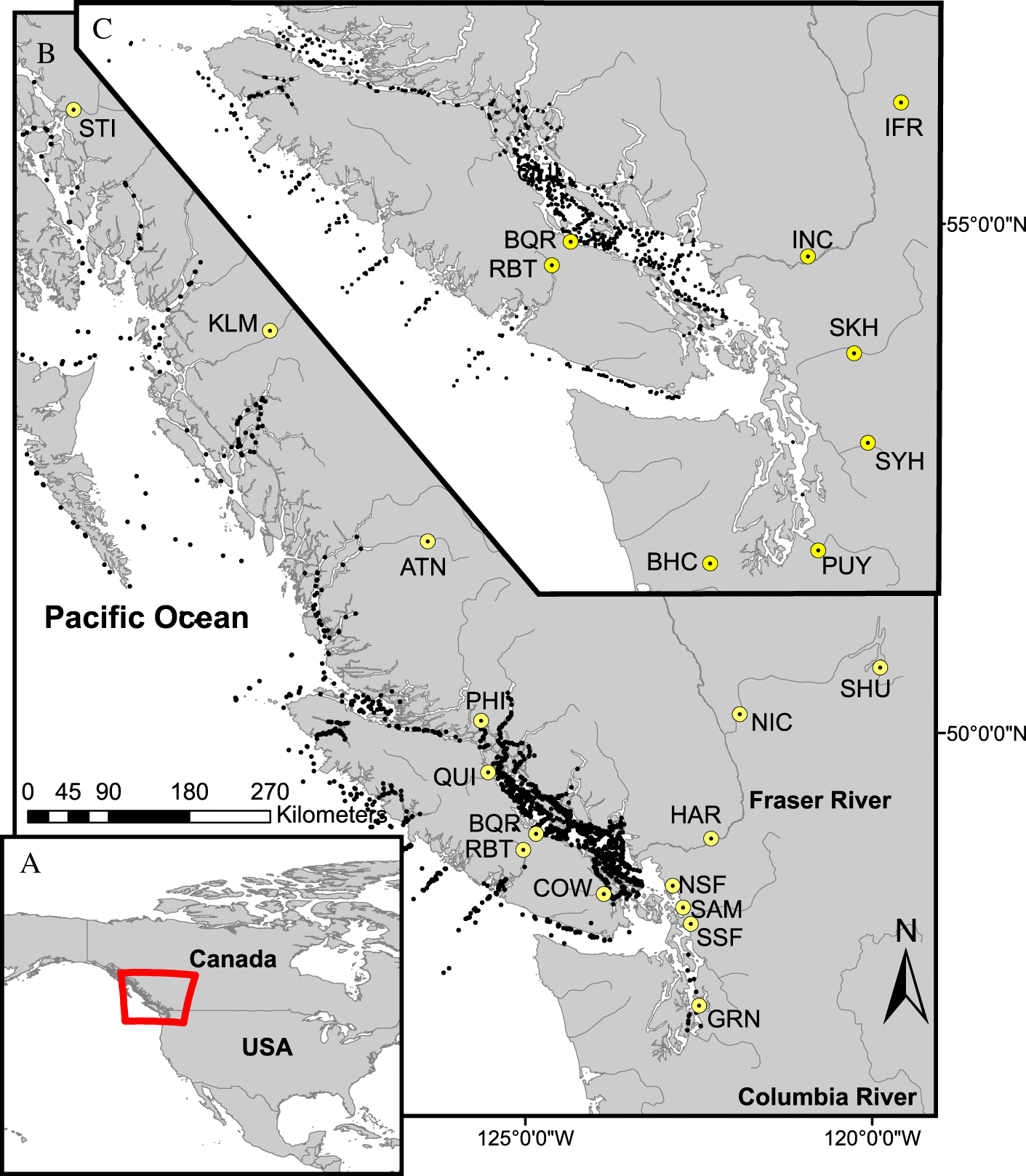
Genetic stock identification
Seasonal division
Molecular methods
| % Chinook positive | % Coho positive | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Taxonomic class or family (viruses) | Spring–summer, n = 2883 | Fall–winter, n = 2836 | Spring–summer, n = 1062 | Fall–winter, n = 997 |
| Renibacterium salmoninarum | Actinobacteria | 2.3 (100) | 0.4 (100) | 1.3 (100) | 0.7 (100) |
| Rickettsia-like organism | Alphaproteobacteria | 3.8 (100) | 6.0 (99) | 2.1 (100) | 0.2 (100) |
| Candidatus Branchiomonas cysticola | Betaproteobacteria | 76.4 (98) | 85.9 (98) | 97.1 (100) | 95.6 (100) |
| Candidatus Piscichlamydia salmonis | Chlamydiae | 0.8 (100) | 0.2 (100) | 1.5 (97) | 0.4 (95) |
| Candidatus Syngnamydia salmonis | Chlamydiae | 27.2 (98) | 17.1 (98) | 17.7 (99) | 13.9 (99) |
| Flavobacterium psychrophilum | Flavobacteriia | 7.9 (98) | 7.4 (98) | 3.1 (99) | 1.7 (99) |
| Tenacibaculum maritimum | Flavobacteriia | 2.8 (62) | 11.6 (62) | 4.8 (98) | 11.1 (98) |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Moritella viscosa | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (3) | 0 (9) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Vibrio anguillarum | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Vibrio salmonicida | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) | 1.8 (99) |
| Yersinia ruckeri | Gammaproteobacteria | 0 (63) | 0 (64) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Piscirickettsia salmonis | Gammaproteobacteria | 0.3 (99) | 1.8 (100) | 0.2 (100) | 0.6 (100) |
| Dermocystidium salmonis | Mesomycetozoea | 0.1 (100) | 0 (100) | 0.6 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Ichthyophonus hoferi | Mesomycetozoea | 11.8 (99) | 23.6 (98) | 10.7 (100) | 8.7 (99) |
| Sphaerothecum destruens | Mesomycetozoea | 1.2 (100) | 2.6 (100) | 2.4 (100) | 4.5 (100) |
| Facilispora margolisi | Microsporea | 5.0 (98) | 11.8 (98) | 5.0 (99) | 7.2 (98) |
| Loma salmonae | Microsporea | 18.5 (99) | 30.4 (98) | 38.2 (99) | 47.7 (98) |
| Paranucleospora theridion (syn. Desmozoon lepeophtherii) | Microsporea | 62.2 (97) | 67.0 (96) | 65.5 (97) | 78.8 (98) |
| Ceratonova shasta | Myxosporea | 24.4 (99) | 22.7 (99) | 10.7 (100) | 5.9 (100) |
| Kudoa thyrsites | Myxosporea | 6.2 (100) | 6.1 (99) | 3.2 (100) | 2.8 (100) |
| Myxobolus arcticus | Myxosporea | 33.8 (99) | 30.8 (98) | 14.9 (99) | 13.0 (99) |
| Myxobolus cerebalis | Myxosporea | 0 (37) | 0 (36) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Myxobolus insidious | Myxosporea | 0.6 (100) | 0.3 (100) | 3.0 (100) | 3.0 (100) |
| Parvicapsula kabatai | Myxosporea | 16.1 (99) | 1.1 (100) | 10.2 (100) | 4.2 (100) |
| Parvicapsula minibicornis | Myxosporea | 33.5 (98) | 36.8 (97) | 40.8 (98) | 36.5 (97) |
| Parvicapsula pseudobranchicola | Myxosporea | 26.2 (97) | 79.5 (97) | 36.5 (96) | 76.9 (97) |
| Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae | Myxosporea | 12.6 (99) | 12.0 (99) | 11.8 (100) | 2.0 (100) |
| Gyrodactylus salaris | Monogenea | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Nanophyetus salmincola | Trematoda | 0.8 (100) | 2.8 (100) | 2.8 (100) | 2.6 (100) |
| Cryptobia salmositica | Kinetoplastida | 0.2 (100) | 0.1 (100) | 2.0 (100) | 2.1 (100) |
| Ichthyophthirius multifiliis | Oligohymenophorea | 14.7 (90) | 8.0 (91) | 5.1 (96) | 4.5 (98) |
| Neoparamoeba perurans | Discosea | 0.1 (100) | 0.6 (100) | 0 (100) | 0.5 (100) |
| Spironucleus salmonicida | Trepomonadea | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Cutthroat trout virus 2 | Hepeviridae | <0.1 (63) | 0 (62) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Salmon alphavirus | Togaviridae | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus | Birnaviridae | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Piscine myocarditis virus | Totiviridae | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Salmon Pescarenavirus 1 | Arenaviridae | 5.0 (62) | 6.5 (61) | 0.3 (100) | 0.2 (100) |
| Salmon Pescarenavirus 2 | Arenaviridae | 0.5 (59) | 0.3 (52) | 0.4 (100) | 0.2 (100) |
| Salmon herpesvirus | Alloherpesviridae | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Infectious salmon anemia virus | Orthomyxoviridae | 0 (40) | 0 (46) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Rainbow trout orthomyxovirus | Orthomyxoviridae | 0 (63) | 0 (62) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy virus | Nodaviridae | 0 (100) | 1.1 (100) | 0 (100) | 0.1 (100) |
| Erythrocytic necrosis virus | Iridoviridae | 15.1 (99) | 20.7 (99) | 6.7 (100) | 10.3 (99) |
| Atlantic Salmon Paramyxovirus | Paramyxoviridae | 0 (37) | 0 (36) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus | Rhabdoviridae | 0.1 (100) | 0.1 (100) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus | Rhabdoviridae | 1.1 (100) | 0.5 (99) | 1.0 (100) | 0.8 (99) |
| Atlantic Salmon Calicivirus | Caliciviridae | 0.1 (63) | 0.4 (63) | 0.2 (100) | 0.4 (100) |
| Pacific salmon nidovirus | Coronaviridae | 9.6 (60) | 0.2 (54) | 0.7 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Salmon gill pox virus | Poxviridae | 0 (63) | 0 (63) | 0 (74) | 0 (86) |
| Pacific salmon parvovirus | Parvoviridae | 0.4 (95) | 0.5 (94) | 0.5 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Chinook aquareovirus | Reoviridae | 0 (63) | 0 (62) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
| Piscine orthoreovirus | Reoviridae | 5.3 (100) | 5.0 (100) | 9.6 (100) | 2.3 (100) |
| Putative Narna-like virus | Unclassified Narnaviridae | 0 (63) | 0 (63) | NA (0) | NA (0) |
| Putative RNA virus 1 | Unclassified | 0.3 (60) | 3.6 (54) | 0.8 (100) | 0.7 (100) |
| Putative toti-like virus | Unclassified Totiviridae | 0 (62) | 0 (62) | 0 (100) | 0 (100) |
Note: Agent names in boldface were detected in this study. The percent of the assayed samples that tested positive for each season are given with the percent of the total sample that was assayed in parentheses. Primer and probe sequences are available in Supplementary Material 1, Table S1. To best describe the taxonomic group of each agent we listed species by class for prokaryotic and eukaryotic agents or by (expected) family for viruses.
Statistical analyses
Pathogen associations with variation in cohort survival
Pathogen associated mass deviation
Model fitting and inference
Results
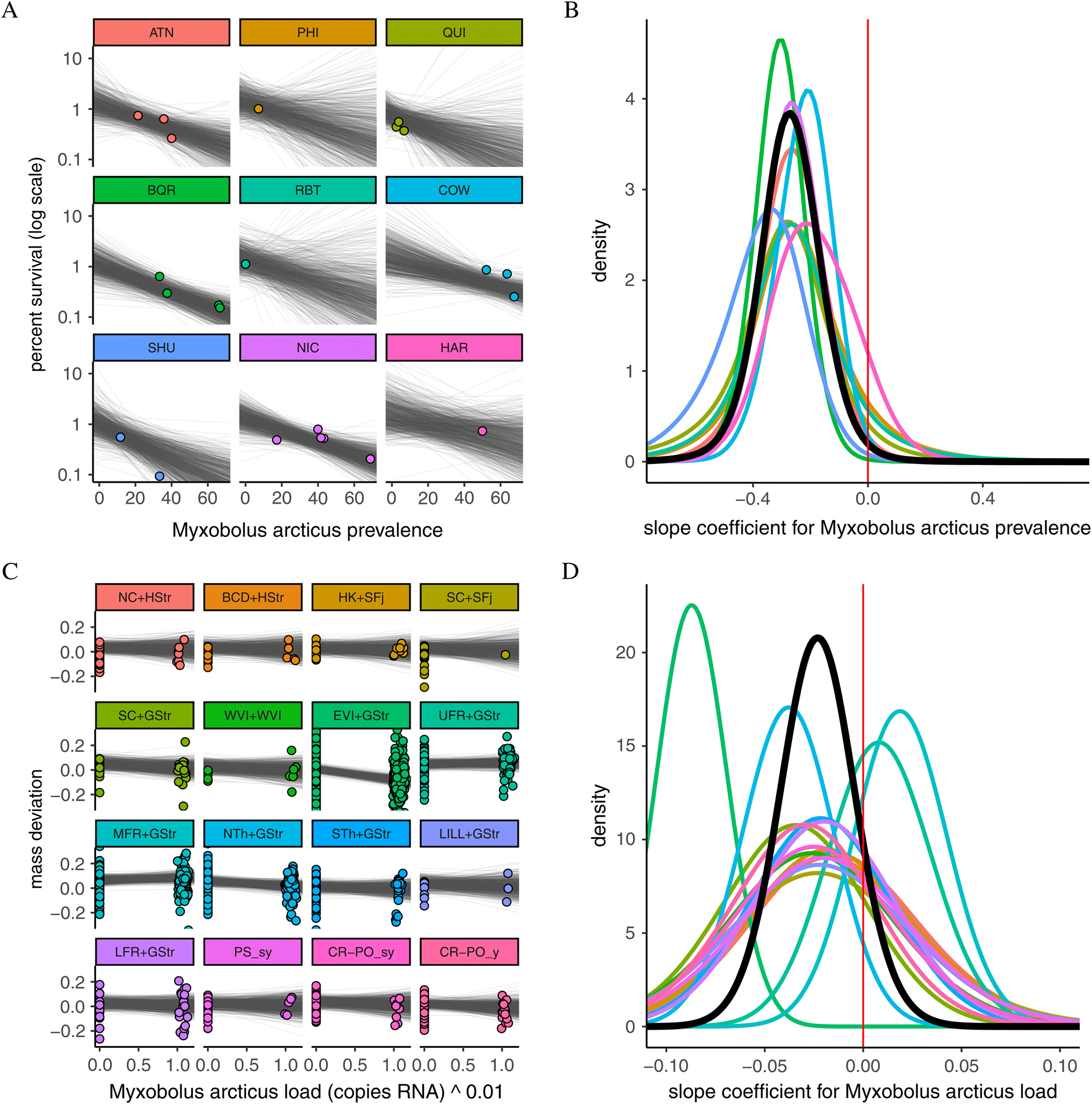
Cohort survival
Mass deviation
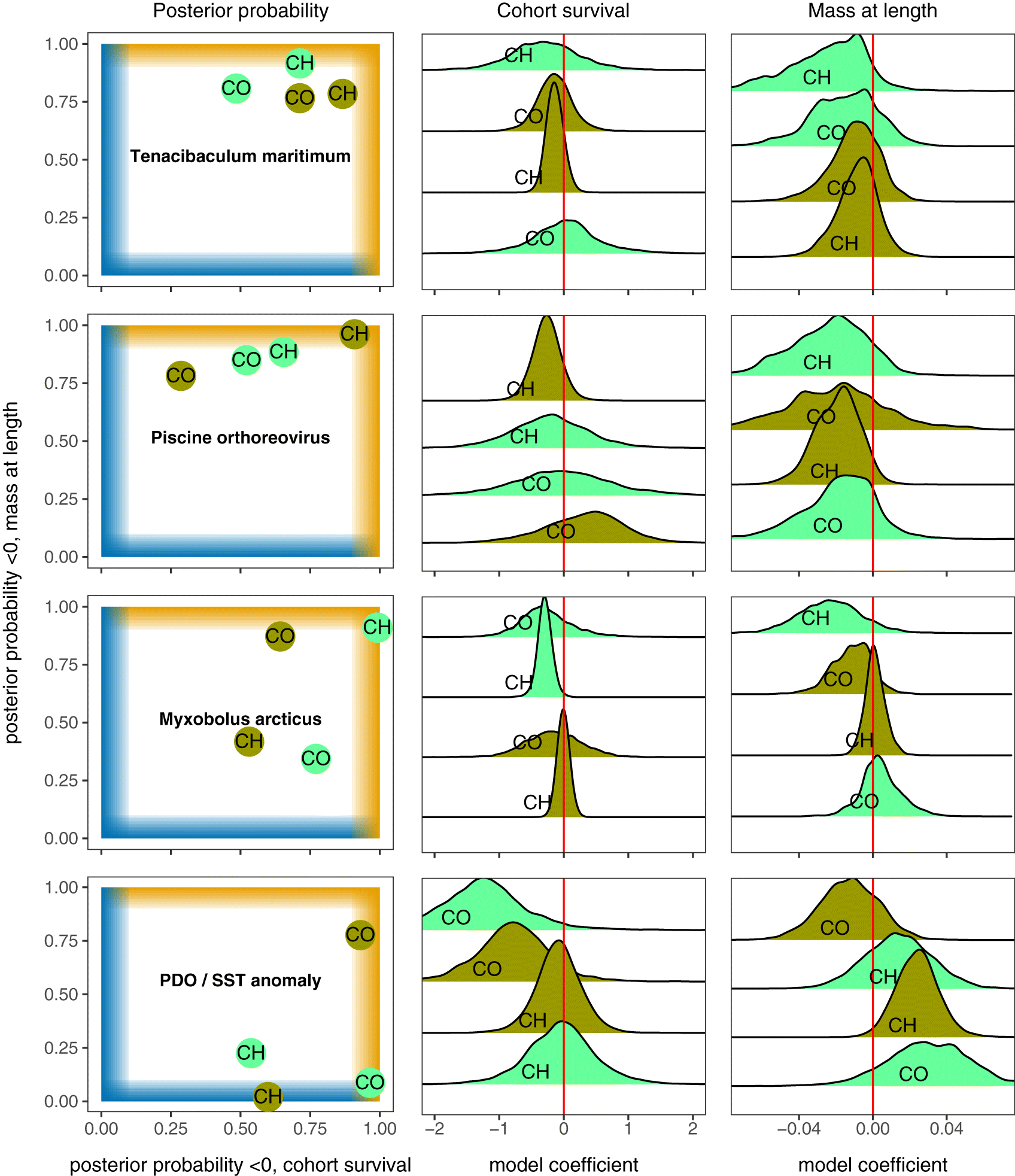
Pathogens with consistent patterns
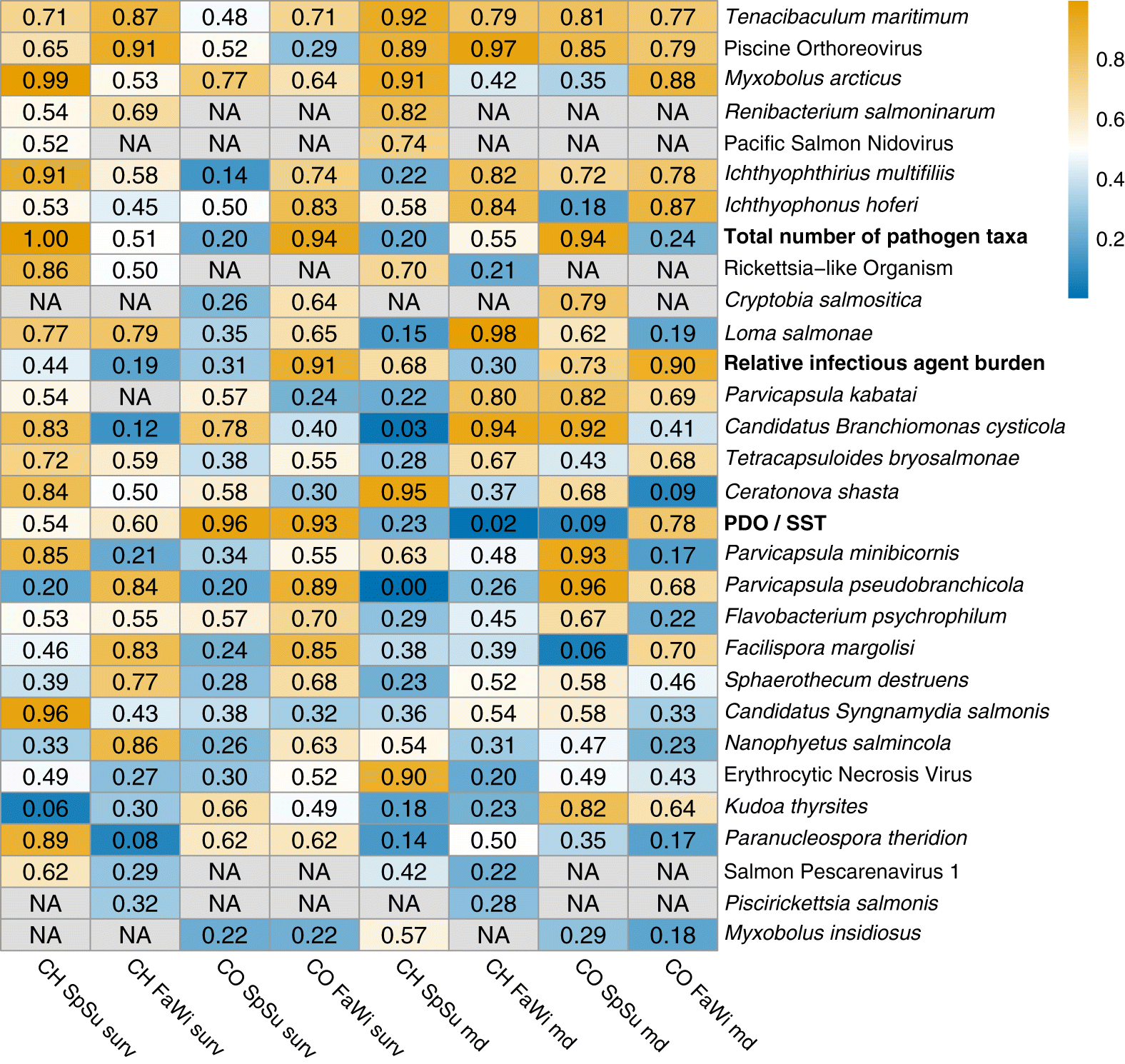
Coinfection variables
PDO and sea surface temperature
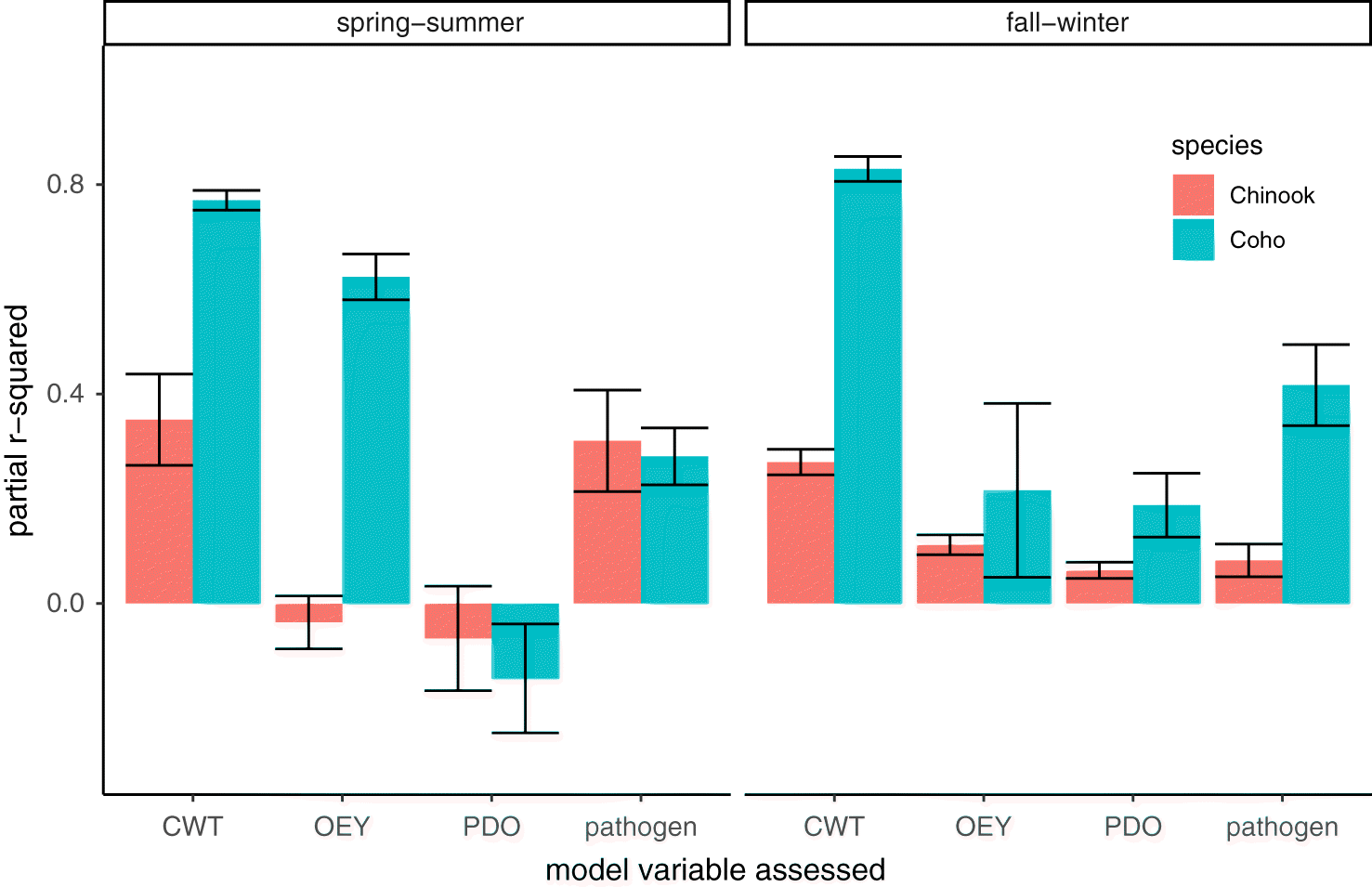
Variance explained by model components
Discussion
Infectious agents associated with poor survival and condition
Coinfection variables
PDO and sea surface temperature
Variance explained by model components
Study limitations
Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
Supplementary material
- Download
- 654.02 KB
- Download
- 3.85 MB
- Download
- 2.86 MB
- Download
- 10.09 MB
- Download
- 6.37 MB
Information & Authors
Information
Published In

History
Copyright
Data Availability Statement
Key Words
Sections
Subjects
Plain Language Summary
Authors
Author Contributions
Competing Interests
Funding Information
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Other Metrics
Citations
Cite As
Export Citations
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
